Let's Connect!
Sign up to receive exclusive communications about offerings, events, news, surveys, special offers, and related topics via telephone, email and other forms of electronic communications.

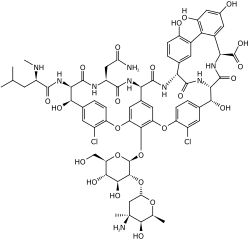
Glycopeptide antibiotic
HYDRANAL™ Laboratory Report L 716 Rev. 1
Vancomycin is extremely hygroscopic. Storage on laboratory atmosphere (approx. 400 mg at 70% rH) led to a weight increase of 0.35% per minute! After 4 days the water content rose from initially 3.2% H2O to 15.6% H2O! Therefore, a quick sample preparation and the use of a weighting spoon with tube is highly recommended.
Vancomycin is not soluble in alcoholic media. Nevertheless, in methanol it is possible to determine the water content of the suspension. In contrast to ethanol, methanol is able to extract the water from the powdered vancomycin sample (see Fig. 1).1We do not recommend this method if the sample forms visible cluster in the solvent.
With the addition of formamide to methanolic solutions it is possible to fully dissolve Vancomycin. This leads on the one hand to accelerated titrations and on the other hand it ensures that all of the sample containing water is titrated.
The basic structure of Vancomycin contains several amine groups. It is well known that amines can react with KF reagents in relation to their basicity. This iodine consuming reaction might lead to random or even missing titration end points.2
Our sample showed just a weak side reaction that was visible as a slightly higher drift. There were no titration difficulties if Hydranal-Composite 5 or Titrant 5 were used. But using Hydranal-Composite 2 or Titrant 2 resulted in random titration end points. However, the side reaction can be suppressed by using Hydranal-Buffer for Bases or adding Salicylic acid to the titration vessel (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
Due to the weak solubility of Vancomycin in ethanol, we do not recommend the use of ethanolic reagents such as Hydranal-CompoSolver E. Even the addition of formamide did not sufficiently increased the solubility.
It is also possible to perform the measurement with a Karl Fischer oven at 120°C (see Fig. 3).
The water content of our sample was 3.2% H2O.
1 A huge disadvantage is that the titration vessel has to be cleaned after each measurement with formamide. Otherwise, disturbing deposits on the titration vessel and on the indicator electrode might interfere with the next measurement.
2 For supplemental information concerning the titration of amines see Lab Report L288.
Procedure for volumetric one-component titration:
Add 30 mL Hydranal-Methanol dry (or Hydranal-Methanol Rapid), 10 mL Hydranal-Formamide dry and 2 g Hydranal-Salicylic acid to the titration vessel and titrate to dryness with Hydranal-Composite 2. Precisely weigh-in approx. 0.2 mg sample using differential weighing and titrate the water content with Hydranal-Composite 2.
Procedure for volumetric two-component titration:
Add 30 mL Hydranal-Solvent, 10 mL Hydranal-Formamide dry and 2 g Hydranal-Salicylic acid to the titration vessel and titrate to dryness with Hydranal-Titrant 2.3 Precisely weigh-in approx. 0.2 mg sample using differential weighing and titrate the water content with Hydranal-Titrant 2.
Please note: Mixtures of alcohol and formamide should be prepared freshly every day. If the mixture is stored longer than 2 days, undesirable side reactions can occur.
Procedure for coulometric titration:
Not advisable.
Procedure for indirect coulometric titration with KF oven:
A cell without diaphragm is often used for the coulometric determination in combination with the KF oven. Place 150 mL of Hydranal-Coulomat AG-Oven in the anode compartment. A cell with diaphragm additionally requires Hydranal-Coulomat CG in the cathode compartment.
After the machine is switched on, it automatically titrates the reagent to dryness. Switch on the carrier gas at a low and stable drift (<10 µg H2O/min).
Prior to the first measurement, we recommend a conditioning time of approximately 30-60 min (carrier gas should be switched on).
Perform the determination of the blank value of an empty injection vial at 120°C (in triplicate).
Weighed in precisely by means of differential weighing approx. 15 mg of Vancomycin hydrochloride to the vial and measure in accordance with the device instruction at 120°C (in triplicate).
Note: The drift value should be stable and low between each measurement. It should be comparable to the original drift value that was observed with carrier gas. Make sure that the automatic drift correction is turned on.
Hydranal-Molecular Sieve 0.3 nm or Hydranal-Humidity Absorber are well-suited as a drying agent for the carrier gas.
3 The addition of Salicylic acid may be omitted if Hydranal-Composite 5 or Titrant 5 are used.
4 Since coulometric cells are very sensitive, the opening of the vessel should be prevented. For the analysis of solids we generally recommend the direct volumetric procedure or the indirect coulometric titration with the KF oven
Hydranal-Water Standard 1.0 is suitable for checking the functional accuracy of the coulometric cell. Hydranal-Water Standard KF Oven 220-230°C or Hydranal-Water Standard KF Oven 140-160°C are suitable for checking the KF oven.
Note: A Suitability test including protocol according to Ph. Eur. is available on request (hydranal@honeywell.com).
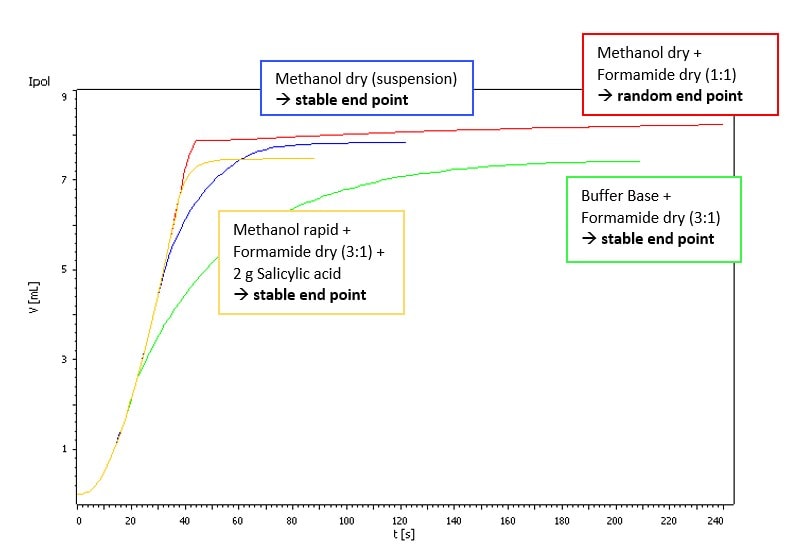
Fig. 1.Titration of approx. 0.5 g Vancomycin HCl in different solvents with Hydranal-Composite 2.
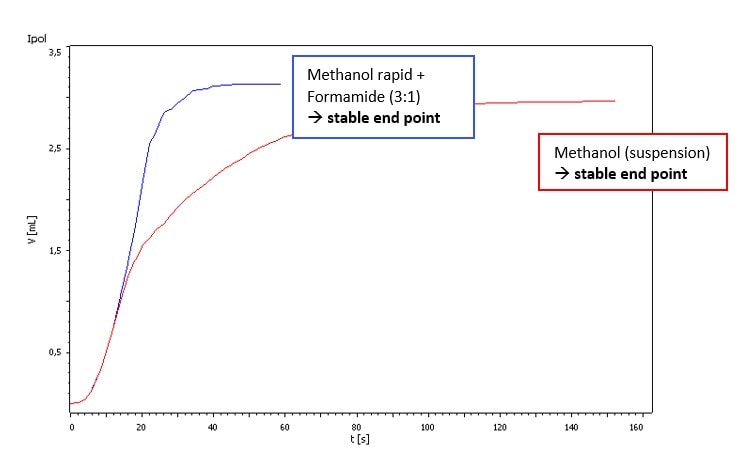
Fig. 2. Titration of approx. 0.5 g Vancomycin HCl in different solvents with Hydranal-Composite 5.
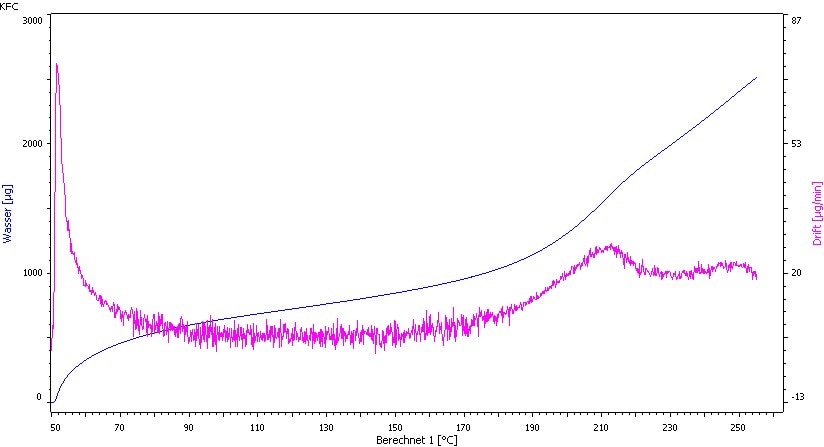
Fig. 3. Temperature ramp of Vancomycin HCl: 50 − 250°C; 1°C/min. Decomposition starts at approx.150°C.